
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Nanophotonics Research Center, Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Micro-Scale Optical Information Technology & Institute of Microscale Optoelectronics, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
The optical vortex beam has widely been studied and used because of its unique orbital angular momentum (OAM). To generate and control OAM in compact and integrated systems, many metallic metasurface devices have been proposed, however, most of them suffer from the low efficiency. Here, we propose and experimentally verify a high-efficiency monolayer metallic metasurface composed of semicircular nano-grooves distributed with detour phase. The metasurface can generate single or an array of OAM with spin-sensitive modulation and achieve the maximum efficiency of 60.2% in theory and 30.44% in experiment. This work has great potential in compact OAM detection and communication systems.
optical vortex orbital angular momentum monolayer metallic metasurface Chinese Optics Letters
2022, 20(12): 123601
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Nanophotonics Research Center, Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Micro-Scale Optical Information Technology & Institute of Microscale Optoelectronics, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
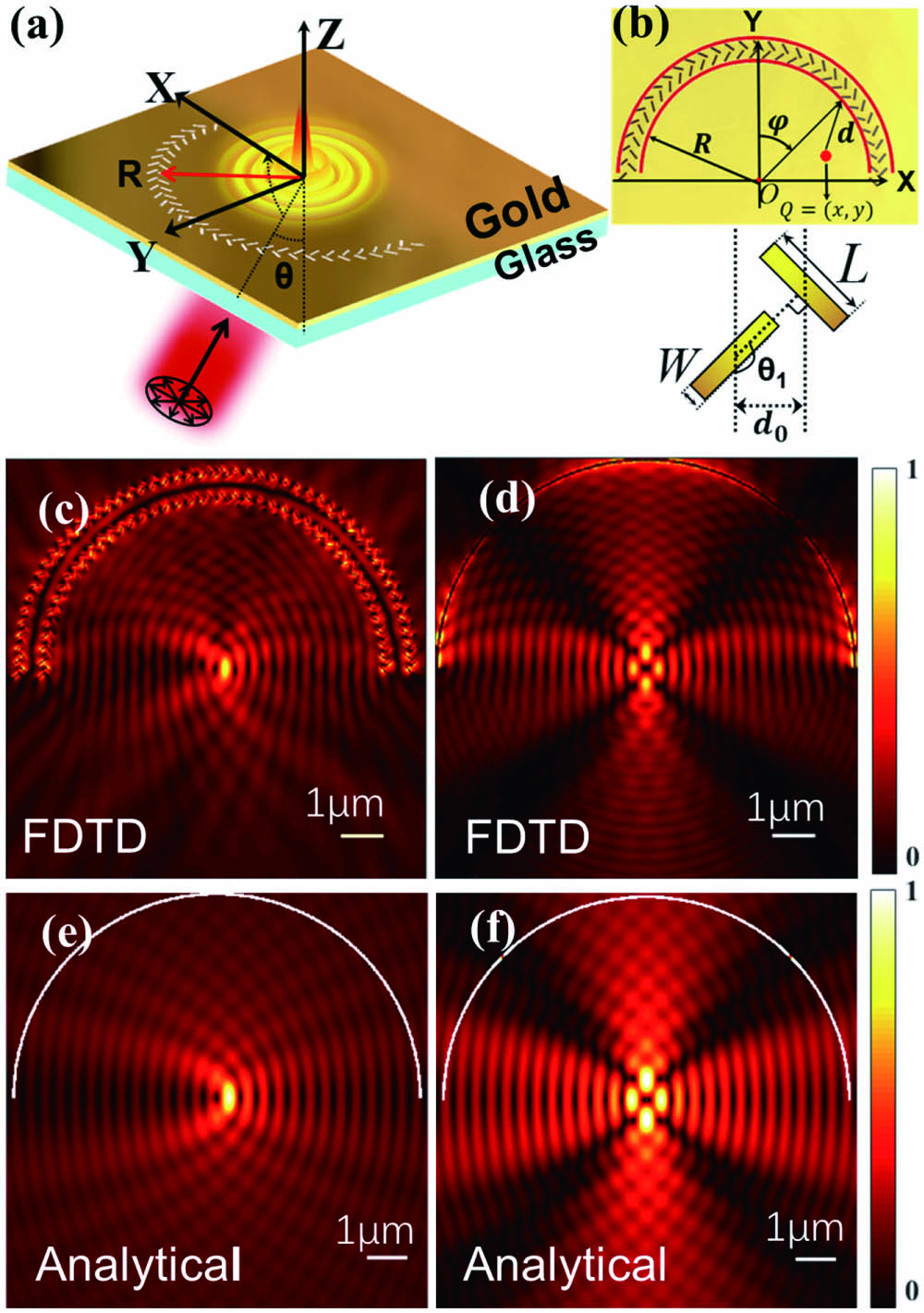
The cylindrical vector beam (CVB) has been extensively studied in recent years, but detection of CVBs with on-chip photonic devices is a challenge. Here, we propose and theoretically study a chiral plasmonic lens structure for CVB detection. The structure illuminated by a CVB can generate single plasmonic focus, whose focal position depends on the incident angle and the polarization order of CVB. Thus, the incident CVB can be detected according to the focal position and incident angle and with a coupling waveguide to avoid the imaging of the whole plasmonic field. It shows great potential in applications including CVB-multiplexing integrated communication systems.
cylindrical vector beam surface plasmon polaritons metasurface optical vortices Chinese Optics Letters
2022, 20(2): 023602
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Nanophotonics Research Center, Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Micro-Scale Optical Information Technology, Shenzhen University, Shenzhen 518060, China
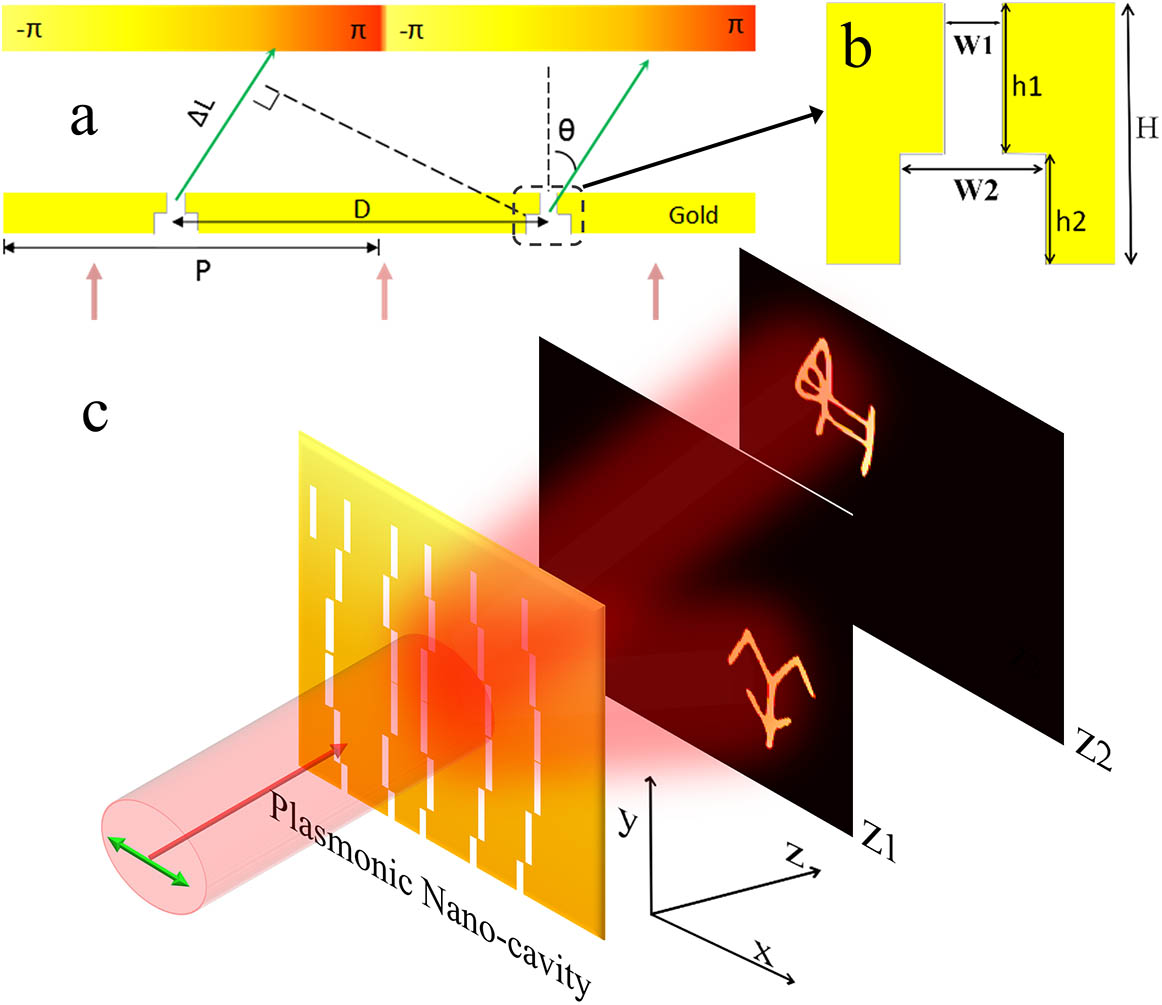
Controlling both amplitude and phase of light in the subwavelength scale is a challenge for traditional optical devices. Here, we propose and numerically investigate a novel plasmonic meta-hologram, demonstrating broadband manipulation of both phase and amplitude in the subwavelength scale. In the meta-hologram, phase modulation is achieved by the detour phase distribution of unit cells, and amplitude is continuously modulated by a T-shaped nano-cavity with tunable plasmonic resonance. Compared to phase-only holograms, such a meta-hologram could reconstruct three-dimensional (3D) images with higher signal-to-noise ratio and better image quality, thus offering great potential in applications such as 3D displays, optical communications, and beam shaping.
240.6680 Surface plasmons 160.3918 Metamaterials 090.2890 Holographic optical elements Chinese Optics Letters
2019, 17(6): 062402
1 西南交通大学牵引动力国家重点实验室, 四川 成都 610031
2 中国科学院上海应用物理研究所上海同步辐射光源, 上海 201204
3 中国科学院高能物理研究所北京同步辐射装置, 北京 100049
通过激光-熔化极稀有气体保护电弧(MIG)复合焊得到了7020铝合金焊接接头,基于电子背散射衍射技术和高精度同步辐射X射线成像等,研究了该接头微观组织、力学性能、疲劳行为及断裂机制。结果表明,在焊接热循环作用下,冷却后复合焊接头各区域的晶粒形态、尺寸及组织成分发生了明显变化。接头静载抗拉强度和屈服强度分别为265.34 MPa和218.85 MPa,接头强度系数为0.74。在50%存活率下,当疲劳寿命为2×106循环周次时,复合焊接头的疲劳强度为96.13 MPa,约为母材的63.14%,焊接过程降低了材料的疲劳性能。疲劳裂纹萌生于复合焊接头熔合区表面深约103 μm的缺口处,呈典型I型四分之一椭圆裂纹扩展形貌。在稳定扩展阶段,气孔对疲劳裂纹扩展速率的影响较小。
激光技术 激光焊接 疲劳裂纹扩展 三维X射线成像 有限元模拟 气孔
1 西南交通大学牵引动力国家重点实验室, 成都 610031
2 挪威科技大学结构工程系, 特隆霍姆N-7491, 挪威
3 中国科学院上海应用物理研究所上海同步辐射光源, 上海 201204
利用高精度同步辐射X射线三维成像技术,对激光-电弧复合焊缝的气孔率进行测定,并将其作为GTN损伤模型中的初始孔洞体积分数。通过建立含余高与不含余高的复合焊接接头的细观损伤力学有限元模型,得到了拉伸接头主应力和孔洞体积分数的分布。通过对拉伸断口金相组织进行分析,发现了几何和材料的不连续性是导致接头失效的重要原因。
激光技术 GTN细观损伤模型 激光-电弧复合焊接 7020铝合金 同步辐射X射线 疲劳损伤 中国激光
2016, 43(10): 1002005
1 西南交通大学牵引动力国家重点实验室, 四川 成都 610031
2 上海交通大学材料科学与工程学院, 上海 200240
3 中国科学院上海应用物理研究所上海光源, 上海 201204
基于光学显微镜、扫描电镜、同步辐射X 射线成像、电子背散射衍射技术、显微硬度计、拉伸性能测试以及有限元仿真探讨了光纤激光-脉冲MIG 复合焊接2 mm 厚7020-T651铝合金的微观组织与力学特性。结果表明:焊缝、熔合线和母材分别为粗大等轴树枝晶、粗大柱状晶和典型的轧制组织,紧邻熔合线存在一个约100 μm 宽的等轴细晶区;接头的抗拉强度、屈服强度、延伸率和强度系数分别为260 MPa、213 MPa、4.8%和0.7;强化元素Zn 的蒸发烧损和再分布以及强化相颗粒变异的综合影响,导致焊缝的硬度值最低(75 HV),约为母材的62.5%,但不是导致接头应力集中的重要原因,焊趾区微小缺口才是导致接头疲劳强度降低的根本原因。
材料 织构演变 元素分布 同步辐射光源 疲劳性能 高速列车





